Exploring Annotation Tool Diagnostics
Overview
This page demonstrates complementary aspects of scDiagnostics anomaly detection alongside built-in quality metrics from the four major annotation tools. We systematically compare how annotation confidence scores relate to detected anomalies and explore gene expression patterns in anomalous versus typical cells.
Code location: R/covid/ and R/merfish/ directories contain supplementary analysis scripts that generate all figures and tables shown below.
Part 1: Annotation Quality Overview (COVID-19)
Confidence Score Distributions Across All Cells
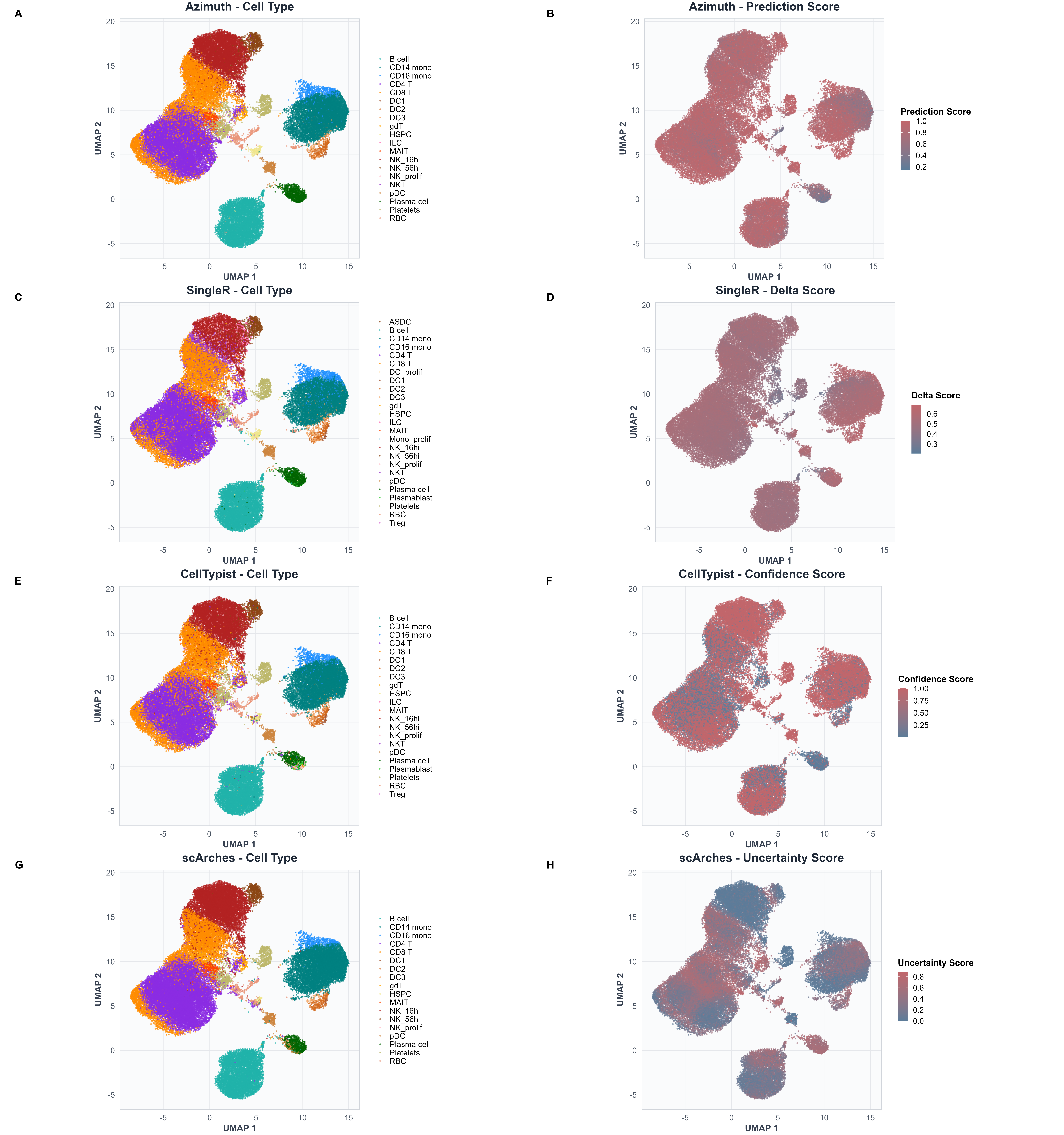
The first visualization provides a comprehensive overview of how each annotation method assigns cell types and confidence scores across the entire dataset.
Script: R/covid/Supplementary_Figure_Code_1.R
What it does:
- Projects all cells into the same dimensionality reduction space (UMAP)
- Colors cells by predicted cell type for each method
- Overlays the method-specific confidence/uncertainty scores
- Creates a 4-row × 2-column comparison (cell type + confidence score per method)
Outputs:
- Fig S1A-B: Azimuth cell types and prediction scores
- Fig S1C-D: SingleR cell types and delta scores
- Fig S1E-F: CellTypist cell types and confidence scores
- Fig S1G-H: scArches cell types and uncertainty scores
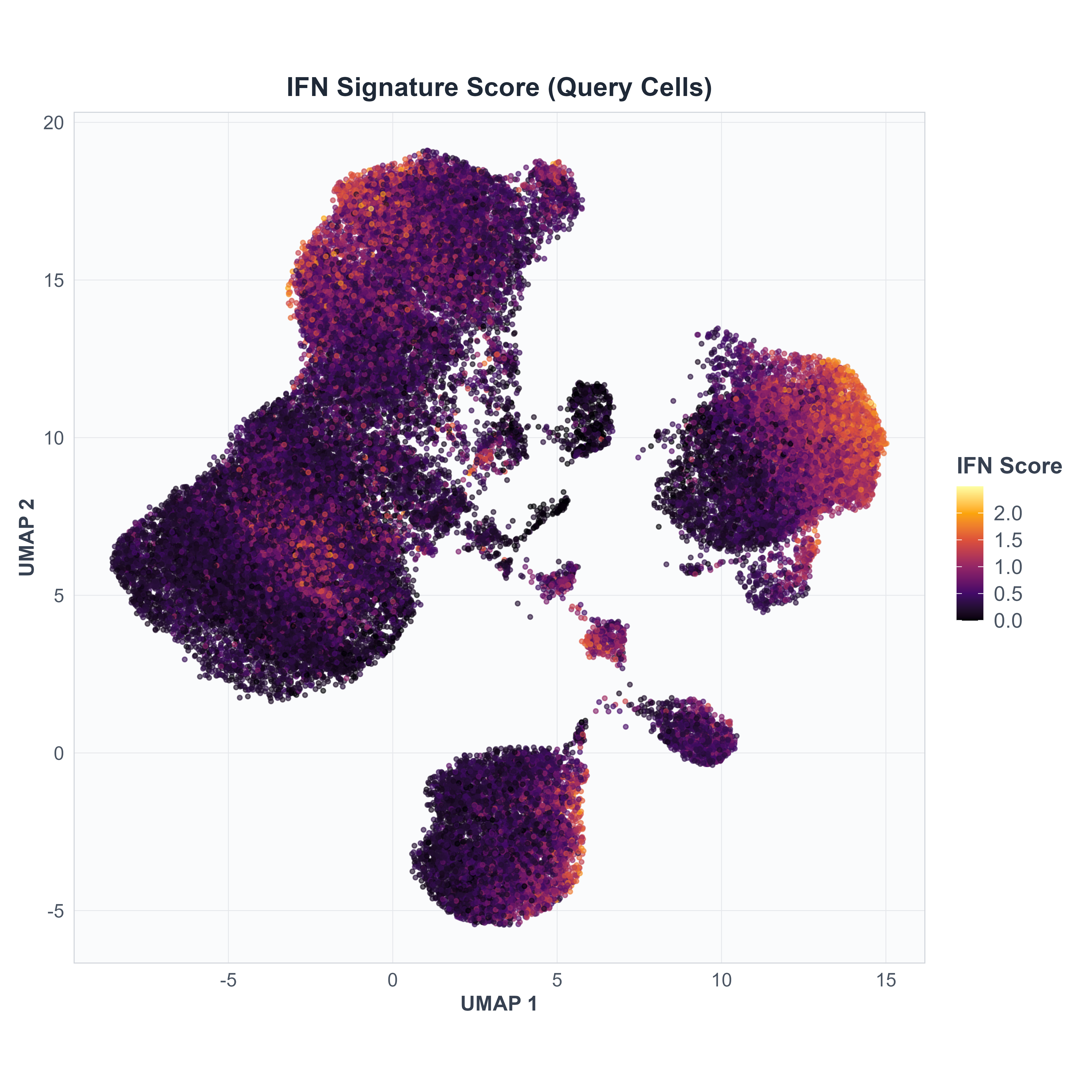
Disease-Associated Signature Expression
The interferon (IFN) signature provides a biological marker of disease state independent of annotation method.
Script: R/covid/Supplementary_Figure_Code_2.R
What it does:
- Calculates mean expression of 25 interferon-responsive genes (Yoshida et al. signature)
- Visualizes IFN score distribution across the UMAP projection
- Shows high expression in immune-activated cells
Output:
- Fig S2: IFN signature score across all query cells
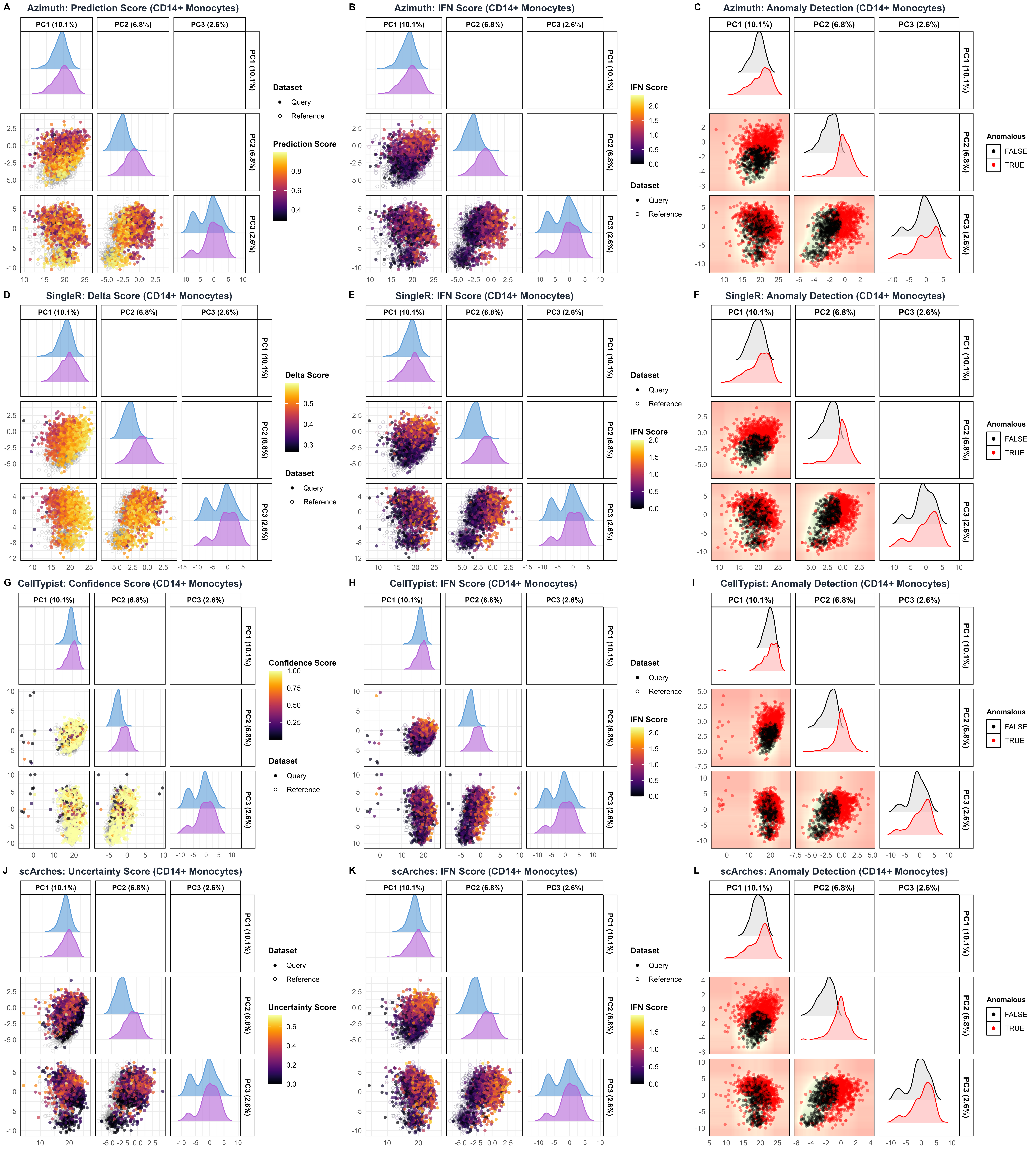
Part 2: Anomaly Detection & Annotation Confidence (COVID-19)
Principal Component Analysis with Confidence Scores
This analysis projects both reference and query cells into shared PCA space and examines how annotation confidence relates to position in this space.
Script: R/covid/Supplementary_Figure_Code_3.R
What it does:
- Projects healthy reference and COVID query cells into PCA space
- For each annotation method:
- Left panel: PCA with points colored by confidence/uncertainty scores
- Middle panel: PCA with points colored by IFN signature score
- Right panel: PCA with anomalous cells highlighted in red
- Focuses on CD14+ monocytes as a well-defined, abundant cell type
- Creates ridge density plots on diagonal to show score distributions
- Generates 4-row × 3-column grid (one row per method)
Key observations:
- Reference cells cluster tightly; query cells show wider scatter
- High-confidence query cells tend to cluster near reference cells
- Anomalous cells detected by isolation forests often occupy peripheral positions in PCA space
Outputs:
- Fig S3A-C: Azimuth (prediction score, IFN score, anomalies)
- Fig S3D-F: SingleR (delta score, IFN score, anomalies)
- Fig S3G-I: CellTypist (confidence score, IFN score, anomalies)
- Fig S3J-L: scArches (uncertainty score, IFN score, anomalies)
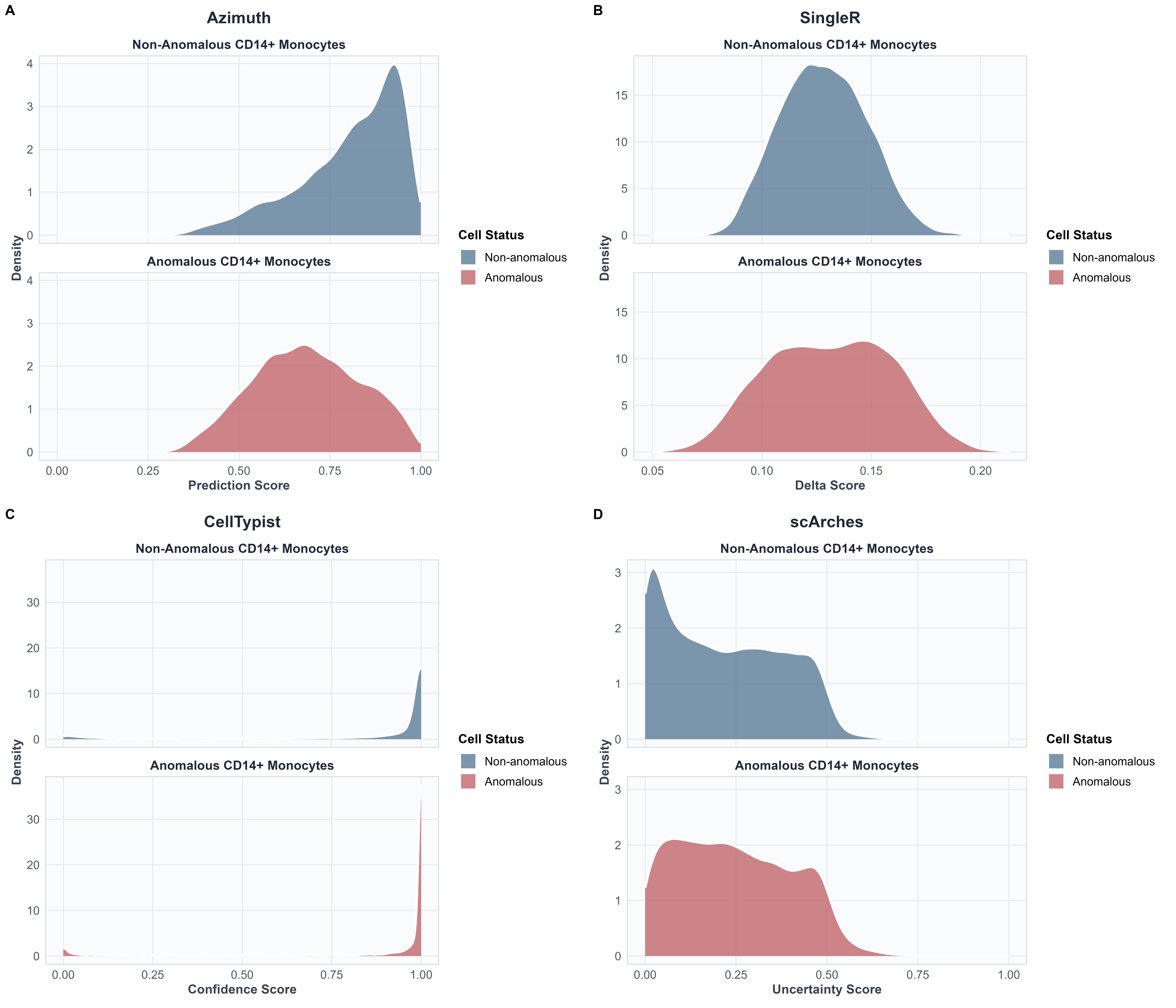
Confidence Score Distributions by Anomaly Status
This analysis directly examines whether annotation confidence scores differ between cells detected as anomalous versus typical.
Script: R/covid/Supplementary_Figure_Code_4.R
What it does:
- Stratifies CD14+ monocytes by anomaly status (anomalous vs. non-anomalous)
- For each annotation method:
- Creates density plots of confidence scores for each group
- Enables visual comparison of score distributions
- Tests for significant differences (Wilcoxon rank-sum test)
- Creates 2-row × 2-column grid (one column per method)
Key observations:
- Anomalous cells typically have lower confidence scores
- Distribution shifts are method-dependent
- Some methods show stronger separation than others
Outputs:
- Fig S4A: Azimuth prediction scores
- Fig S4B: SingleR delta scores
- Fig S4C: CellTypist confidence scores
- Fig S4D: scArches uncertainty scores
Part 3: Gene Expression Patterns in Anomalies (COVID-19)
Interferon Gene Expression Shifts
This comprehensive analysis examines how interferon-responsive genes are dysregulated in anomalous cells.
Script: R/covid/Supplementary_Figure_Code_5.R
What it does:
- For each annotation method, stratifies CD14+ monocytes by:
- Left column: Annotation tool confidence quantiles (high vs. low confidence query cells)
- Right column: scDiagnostics anomaly detection (anomalous vs. non-anomalous query cells)
- Calculates pseudo-bulk log₂ fold changes relative to reference
- Displays fold changes for all 25 interferon genes
- Correlates gene expression patterns between the two stratification approaches
- Creates 4-row × 2-column grid (one row per method)
Key observations:
- Strong concordance between confidence-based and anomaly-based stratifications
- Anomalous cells show elevated IFN gene expression
- Low-confidence cells also exhibit IFN upregulation
- Gene patterns are consistent across annotation methods
Outputs:
- Fig S5A-B: Azimuth (confidence quantiles, anomaly detection)
- Fig S5C-D: SingleR (confidence quantiles, anomaly detection)
- Fig S5E-F: CellTypist (confidence quantiles, anomaly detection)
- Fig S5G-H: scArches (confidence quantiles, anomaly detection)

Part 4: Spatial Annotation Overview (MERFISH)
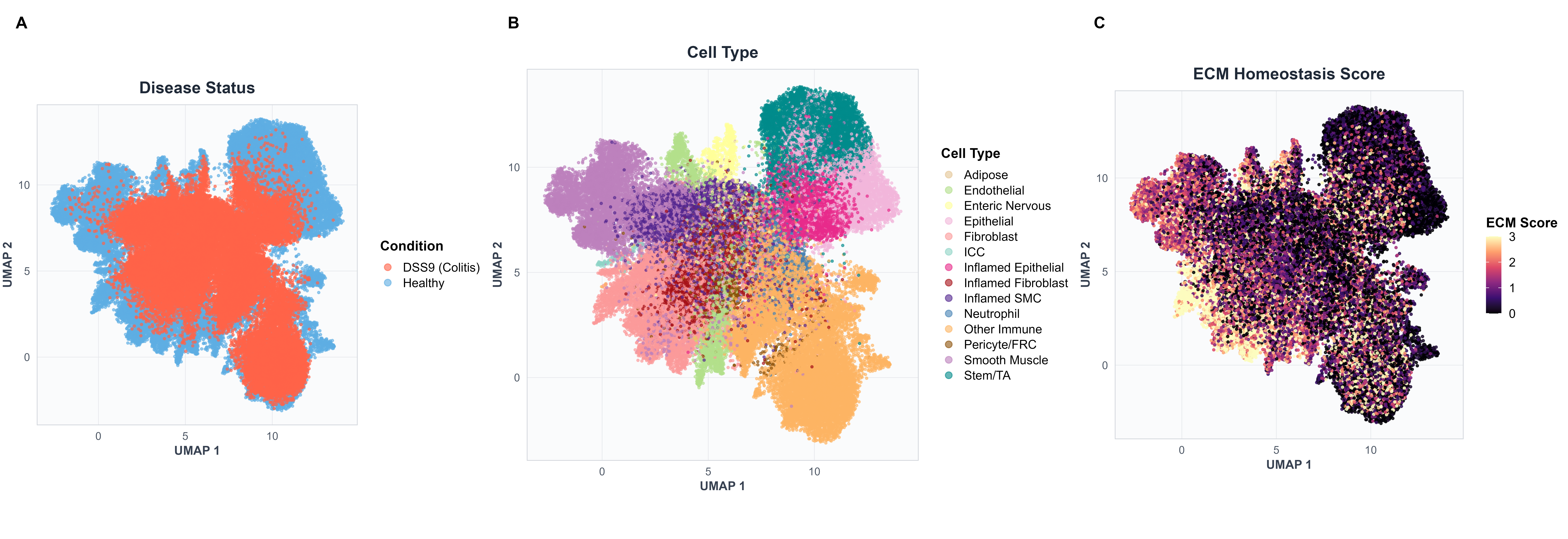
Disease State and Cell Type Distribution
This analysis provides an overview of the spatial landscape in healthy versus inflamed colon tissue.
Script: R/merfish/Supplementary_Figure_Code_1.R
What it does:
- Projects all cells into UMAP space (computed from scVI latent space)
- Visualizes disease status (healthy vs. DSS9 day 9 colitis)
- Shows cell type spatial distribution
- Overlays ECM homeostasis score computed from five key fibroblast genes
Outputs:
- Fig S6A: Disease status across combined UMAP
- Fig S6B: Cell type annotations across combined UMAP
- Fig S6C: ECM homeostasis score distribution
Spatial Annotation Patterns
This analysis examines how each annotation method assigns cell types and confidence scores across the spatial tissue organization.
Script: R/merfish/Supplementary_Figure_Code_2.R
What it does:
- Projects all four annotation methods (Azimuth, SingleR, CellTypist, scArches) onto spatial coordinates
- For each method: displays predicted cell types and method-specific confidence/uncertainty scores
- Creates 4-row × 2-column grid (one row per method)
- Enables direct visual inspection of spatial annotation patterns and score distributions
Key observations:
- Annotation agreement generally high in major cell types
- Confidence scores vary spatially, with lower scores at tissue boundaries or in rare cell types
- Methods show slightly different spatial patterns reflecting their different statistical approaches
Outputs:
- Fig S7A-B: Azimuth cell types and prediction scores (spatial)
- Fig S7C-D: SingleR cell types and delta scores (spatial)
- Fig S7E-F: CellTypist cell types and confidence scores (spatial)
- Fig S7G-H: scArches cell types and uncertainty scores (spatial)
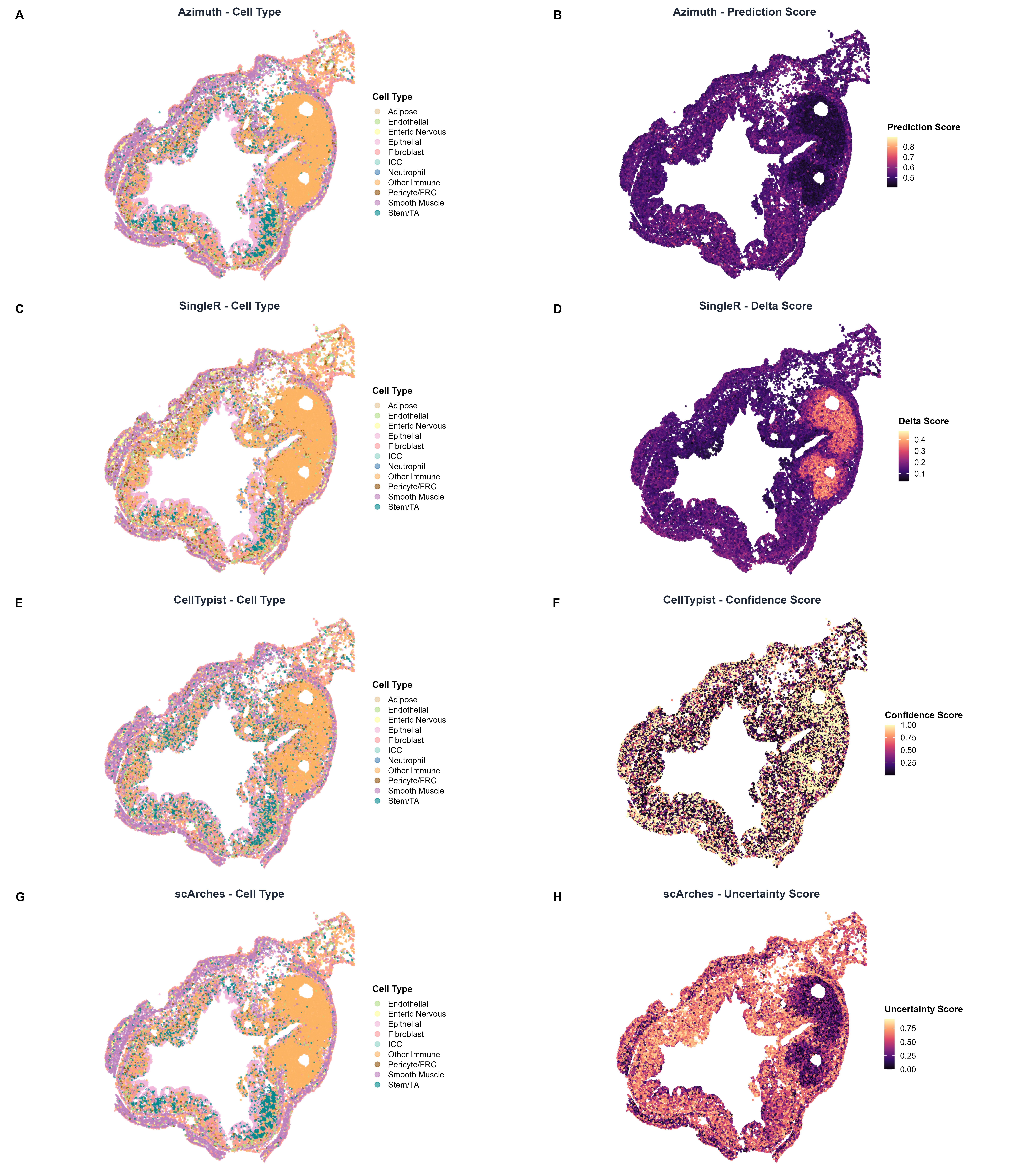
Part 5: Anomaly Detection in Spatial Data (MERFISH)
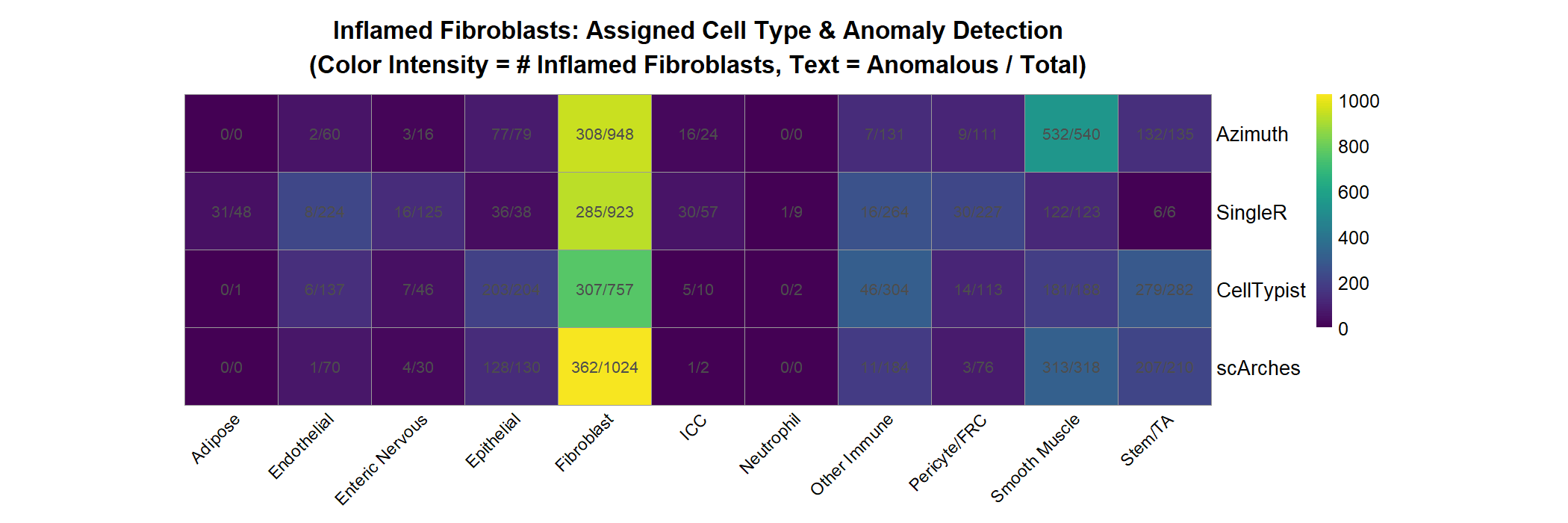
Inflamed Fibroblast Classification
This analysis focuses on a key disease-associated cell state: inflamed fibroblasts (IAFs), which are expanded in DSS-induced colitis.
Script: R/merfish/Supplementary_Figure_Code_3.R
What it does:
- Identifies all inflamed fibroblasts (ground truth from reference annotation)
- For each annotation method, determines how IAFs are classified:
- How many are correctly identified as fibroblasts?
- How many are misclassified as other cell types?
- Runs
scDiagnosticsanomaly detection on each method’s predictions - Creates heatmap showing IAF distribution across predicted cell types
- Text shows proportion of cells detected as anomalous
Key observations:
- Most methods predict majority of IAFs as fibroblasts (high sensitivity)
- Some IAFs classified as smooth muscle cells (method-dependent misclassification)
- scDiagnostics anomaly detection flags many IAFs as outliers, even when correctly classified
Output:
- Fig S8: Heatmap of IAF predictions and anomaly detection across methods
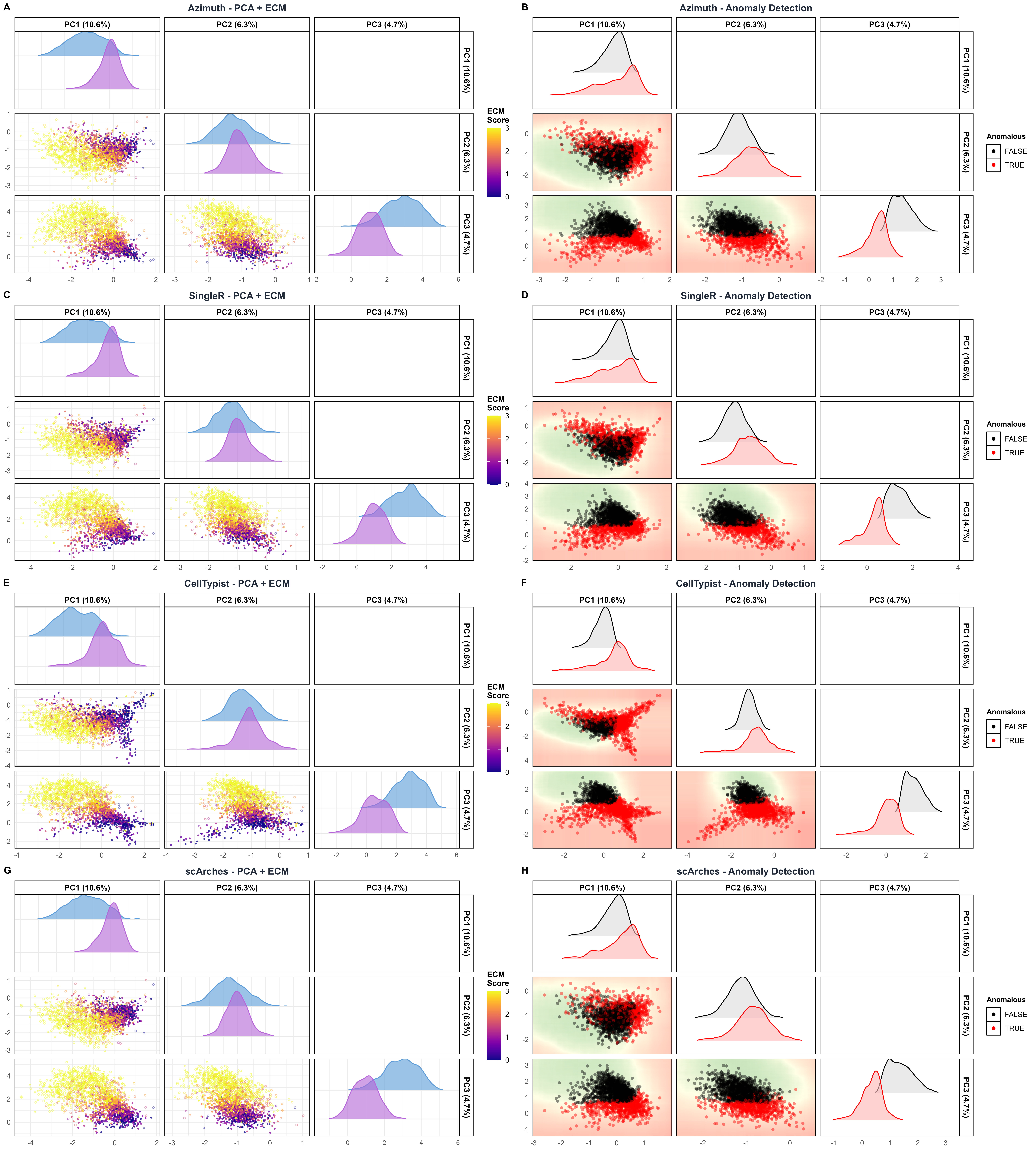
PCA Projection with ECM Signature
This comprehensive analysis projects healthy reference and inflamed query fibroblasts into shared PCA space and examines ECM gene expression patterns.
Script: R/merfish/Supplementary_Figure_Code_4.R
What it does:
- Projects reference (healthy) and query (DSS) fibroblasts into PCA space
- For each annotation method:
- Left panel: PCA with points colored by ECM homeostasis score
- Right panel: PCA with anomalous fibroblasts highlighted in red
- Creates 4-row × 2-column grid (one row per method)
- Shows how fibroblasts are positioned relative to reference and whether anomaly detection identifies them
Key observations:
- Inflamed query fibroblasts show higher ECM scores (elevated Col1a2, Timp2, etc.)
- Anomalous cells tend to occupy peripheral positions in PCA space
- Reference fibroblasts cluster tightly; query cells show wider scatter reflecting disease-induced heterogeneity
Outputs:
- Fig S9A-B: Azimuth (PCA + ECM, anomaly detection)
- Fig S9C-D: SingleR (PCA + ECM, anomaly detection)
- Fig S9E-F: CellTypist (PCA + ECM, anomaly detection)
- Fig S9G-H: scArches (PCA + ECM, anomaly detection)
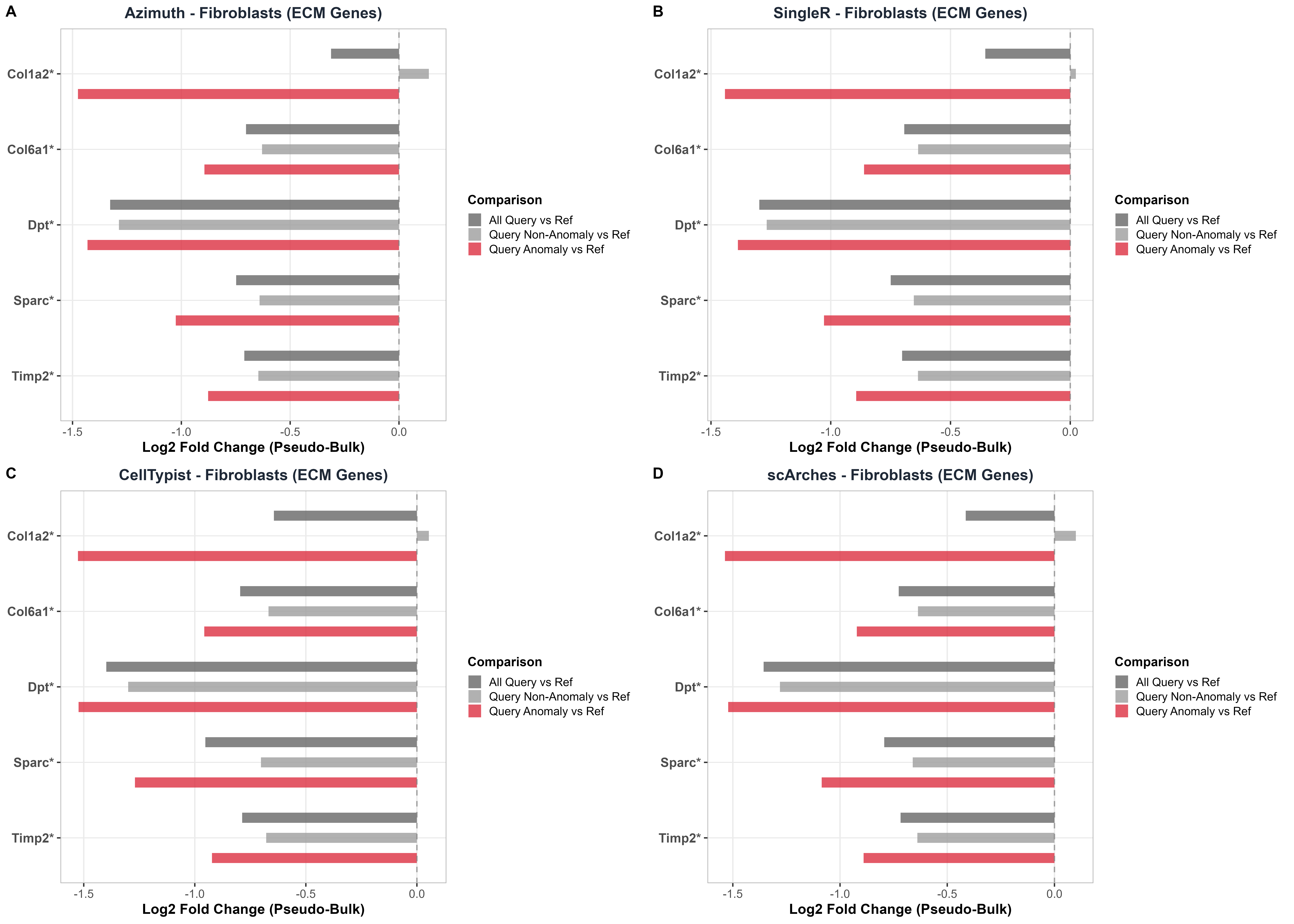
ECM Gene Expression in Anomalies
This final analysis focuses specifically on the five ECM homeostasis genes and how their expression differs between anomalous and typical cells.
Script: R/merfish/Supplementary_Figure_Code_5.R
What it does:
- Analyzes expression of five key ECM genes: Col1a2, Timp2, Col6a1, Sparc, Dpt
- For each annotation method:
- Calculates pseudo-bulk log₂ fold changes relative to healthy reference
- Compares anomalous vs. non-anomalous fibroblasts
- Creates barplot showing gene-by-gene patterns
- Creates 2-row × 2-column grid (one cell per method)
Key observations:
- Anomalous fibroblasts show elevated ECM gene expression across all methods
- Elevation is consistent and robust across the four annotation approaches
- Col1a2 shows particularly strong upregulation in anomalous cells
Outputs:
- Fig S10: ECM gene expression shifts across all four methods
Summary
These comprehensive supplementary analyses demonstrate that:
- COVID-19 scRNA-seq:
- Annotation confidence and anomaly detection are concordant
- Anomalies have distinct molecular signatures (elevated interferon response)
- Patterns are consistent across all four annotation methods
- MERFISH Spatial Data:
- Spatial context reveals how anomalies organize within tissue
- Disease-associated fibroblasts show elevated ECM expression
- Anomaly detection identifies biologically relevant cell states
- Cross-Dataset Findings:
- Annotation confidence scores reliably predict anomaly status
- Gene expression patterns align between confidence-based and anomaly-based stratifications
scDiagnosticscomplements rather than replaces annotation tool scores
Complete Analysis Pipeline
To reproduce all supplementary analyses:
```r # COVID-19 analyses source(“R/covid/Supplementary_Figure_Code_1.R”) source(“R/covid/Supplementary_Figure_Code_2.R”) source(“R/covid/Supplementary_Figure_Code_3.R”) source(“R/covid/Supplementary_Figure_Code_4.R”) source(“R/covid/Supplementary_Figure_Code_5.R”)
MERFISH analyses
source(“R/merfish/Supplementary_Figure_Code_1.R”) source(“R/merfish/Supplementary_Figure_Code_2.R”) source(“R/merfish/Supplementary_Figure_Code_3.R”) source(“R/merfish/Supplementary_Figure_Code_4.R”) source(“R/merfish/Supplementary_Figure_Code_5.R”) ```[end]
All figures and tables are saved to figures/supp/covid/ and figures/supp/merfish/.